Hey, friends!
The bear market is back…just kidding.
But lots of bearish takes on crypto Twitter lately.
Many people believe we have topped for the year, and also seeing people saying we are 60-70% done with this bull run.
Just understand that none of them know how it will end, so you got to think for yourself. Risk accordingly.
Today’s newsletter is a deep dive into Mangrove which is a project I am an investor in.
Btw, they have a quite degen community, make sure to check them out on Twitter too:
Mangrove - Restake DeFi liquidity to earn more on Blast
Introduction
ELI5 TLDR:
Mangrove is a DEX that is EVM-compatible and designed to improve the trading experience in DeFi. Its primary focus is addressing fragmented liquidity , high slippage, and under-utilized capital by providing responsive liquidity.
Mangrove relies on 2 major concepts to achieve reactive liquidity:
Smart offers: unlike locked liquidity pools, the liquidity offered on Mangrove is not restricted to a single pool. If an offer posted on Mangrove remains unmatched, it can generate yield elsewhere on the chain. This liquidity can be left to grow while waiting to be sourced.
Bounty: to prevent Makers from posting offers that are destined to fail, they must include a native token provision (the bounty) in their offer. This provision makes it costly for Makers to post orders that are not intended to be executed. If an offer fails, the bounty is then given to the Taker as compensation.
Okay, let’s dig some deeper in here, anon.
Mangrove is an order book DEX with hooks on Blast L2 that allows liquidity providers to post arbitrary smart contracts (hooks) as offers.
This enables features such as re-staking of liquidity held on other protocols, liquidity amplification and liquidity provision via custom strategies.
Unlike typical DEXs, Mangrove introduces an innovative approach to liquidity and order management, each offer can have its own logic hook and hence a whole new paradigm in orderbooks. On Mangrove, liquidity providers can add logic (code) to their offer.
For developers, it mean a total freedom to build a market making strategy. For UI user, it means being able to post limit orders intents, while sourcing its liquidity from lending protocol, and in the coming weeks, being able to market make while sourcing liquidity from these protocols.
As a Blast Big Bang Winner and one of the DEX with the most activity on Blast, Mangrove received Blast Gold and redistribute 100% of it to its users.
Mangrove's order book DEX lists promises instead of locked commitments (liquidity is not locked on Mangrove). It can be employed elsewhere until the offer is matched.
For example, you can provide liquidity (LP) on another exchange and use this LPed liquidity on Mangrove at the same time to trade or run strategies. This way, you can earn from up to 6 sources of yields, points and spread.
Let’s go further to one of Mangrove’s key features. It’s now possible to run on chain market-making strategies like Kandel. This needs a proper explanation, so let’s go through it.
What is Kandel?
Kandel is an Automated Market Making (AMM) strategy that uses on-chain order flow to repost offers instantly, without any latency. It could be considered as a market-making bot equivalent that operates solely on the blockchain. It leverages the interaction between buyers and sellers that creates price movement, rather than the price itself.
With liquidity that remains in your wallet, you can post offers at different prices on the book, on both sides of the book, depending on your parameters. Anyone can create their own Kandel by visiting: app.mangrove.exchange/strategies
On Kandel, as on Uniswap v3, you have to choose your
(1) the price range
(2) the amount of base—WETH for instance,
(3) the amount of quote—USDB (USD Blast) for instance.
(4) the number of offer posted within your price range (between min and max).
Number of offers is the total offers posted on both side of the book, by your strategy (see example below with 5 offers (2 on the left, 3 on the right).
Order Types:
Market Orders (standard)
Limit Orders: Your normal limit order with a special touch: liquidity sourcing—you can source liquidity from your positions on lending protocols on Blast, such as ZeroLend, Orbit or Pac Finance. You can also source liquidity from your wallet instead of these protocols, as Mangrove doesn’t lock liquidity.
Amplified Orders: post multiple limit orders across different markets using the same liquidity, allowing different strategies. Example: you have 10,000 USDB. You can use Amplified orders to buy either token1 or token2 or token3, each at a different price. Once one of this offer is taken, it’ll update the others (if partially filled), or cancel the order (if entirely filled). This is so cool!
Now, let’s go more in depth into Kandel, let’s look under the hood.
An ELI5 explanation of what Kandel is would be:
Kandel is an on-chain Automated Market Making strategy that focuses on order flow rather than price. It automatically posts Bids and Asks within your chosen market and price range to buy low and sell high, making a profit through the spread.
Features
On-chain market making bot Kandel is a market-making bot equivalent that operates solely on the blockchain. Unlike off-chain market making bots that experience delays, Kandel uses on-chain order flow to repost offers instantly, without any latency.
Profit from the spread: Kandel follows your configuration parameters to populate Bids and Asks offers. When those are taken, the profits are generated from the difference between the two, known as the spread.”
Compounding: you have the opportunity to accumulate profits generated from spreads and reinvest them back into your offers, a process commonly known as compounding (remember compound interest is key for big gains)
Price range: since Kandel is an automated market-making strategy, the price range needs to be set. It consists of the lowest and highest prices in the price grid at which the market maker is willing to post its bids and asks on Mangrove DEX.
Earn extra yield on AAVE: since the liquidity on offer is not locked on the Mangrove order book, it can generate yield elsewhere on the chain. With Kandel, when an offer is taken, your liquidity can be sourced and redeposited on AAVE.
Disruptive Trading Mechanics
Orderbook with Hooks: Mangrove redefines liquidity provision by enabling liquidity providers to attach custom logic to their offers, akin to Uniswap, thus introducing liquidity sourcing.
Liquidity Sourcing: No TVL on Mangrove. The order book can dynamically source liquidity from the entire blockchain, including lending protocols, other DEXs, flash loans, and yield/vault protocols. Right now, on Mangrove, you can post limit offers while your liquidity sits on another protocol such as ZeroLend. Let’s say you are lending your USDB on ZeroLend. You can use it to post a limit order intent on Mangrove. Once it’s executed, Mangrove will fetch (source) the liquidity from ZeroLend, give it to the taker, and redeposit on ZeroLend the resulting capital (or another destination depending on what you did choose). Example: I have 10,000 USDB on ZeroLend, post a limit offer on Mangrove to buy WETH at $3,300 with my 10,000 USDB, with sourcing on ZeroLend, and also deposit on ZeroLend. Once my offer is taken, Mangrove will take my USDB from ZeroLend, give it to the taker, and take the taker funds, deposit it on ZeroLend.
Financial Backing and Future Vision
Strong Venture Capital Support: Mangroe is backed by leading VCs like Wintermute, Gumi Crypto, Cumberland, Greenfield, and CMT Digital, among others. Mangrove has successfully raised more than $10M across Seed and Series A funding rounds.
Strong team: Mangrove has been created by one of the minds behind Morpho and Vincent Danos, while the Mangrove team is composed of former Aave, Paraswap and Nethermind people.
Okay, so far so good. But what is really the difference between Mangrove and other DEXs?
The main difference between Mangrove and other DEXs is the ability to attach code to offers . This translates into several disruptive mechanisms:
Reactive liquidity
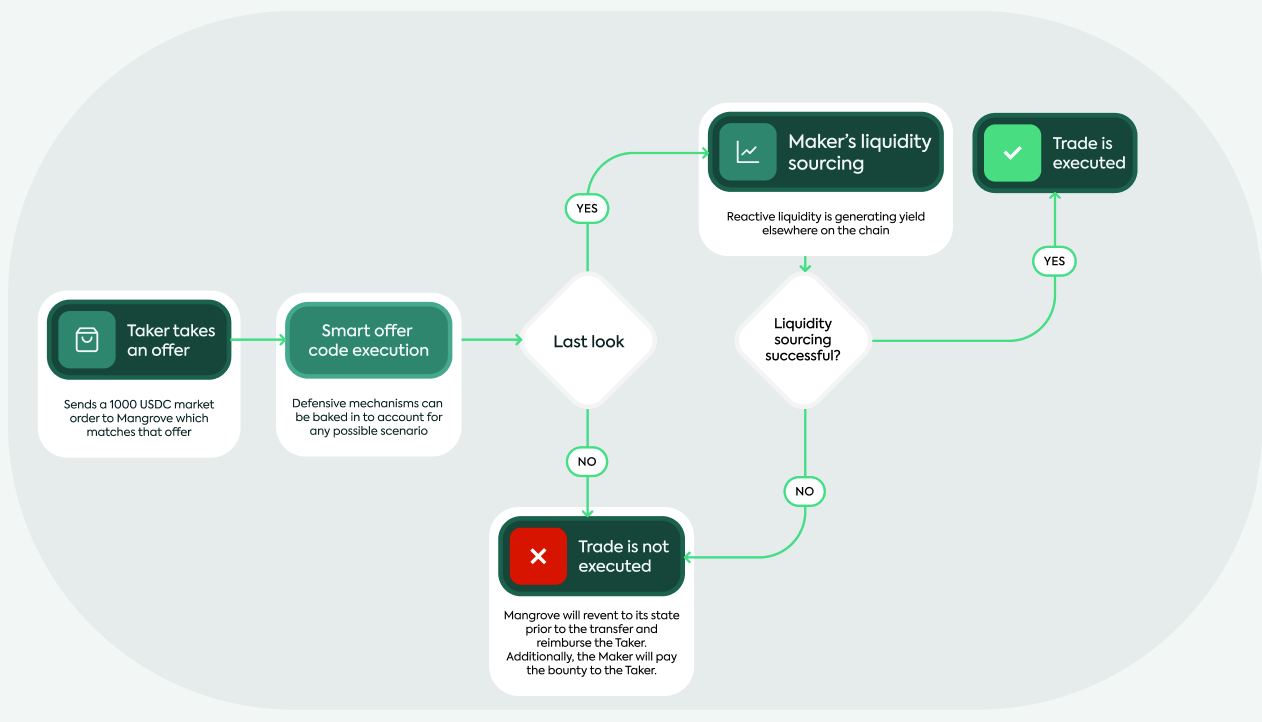
The liquidity on offer on Mangrove is not locked in a pool. As long as an offer posted on Mangrove is not taken, it can generate yield elsewhere on the chain - Aave, Compound or Morpho are great examples of protocols where you could leave your liquidity to grow, waiting to be sourced.Last look
Since an offer contains code, defensive mechanisms can be baked in to cancel a promise previously made:For instance, if the market conditions are not anymore satisfactory at the time the offer is taken VS when it was posted
Code can cover any unwanted case scenarios (ex: high volatility), and therefore can mitigate/solve problems of slippage and arbitrage
Code helps make zero-latency trading decisions, with as much information as available on-chain at the time the trade occurs
Persistence
Through the executed code, the offer can automatically repost itself on the order book. For someone who is posting offers (we call them Makers, or Market Makers), this is very handy because they can immediately update the amount of tokens they are offering after some of it has been taken. People that take offers are called Takers.
Bounty
What if everyone makes empty promises, and the offers in the book are all meant to fail?
This is where Makers must leave a native token provision (the bounty) in their offer. Nothing prevents them from posting offers that will always fail. So, to ensure that the offers displayed on the book are credible, it must be costly for Makers to post orders that are not meant to go through. And in that case scenario, the bounty is then given to the Taker as compensation.
At first, this might appear to favor Makers. However, with advanced market-making features that allow them to accept or cancel offers, Makers can mitigate their risk and offer better prices. Ultimately, both Makers and Takers benefit: the risk of offer failure is essential for the effectiveness of smart offers.
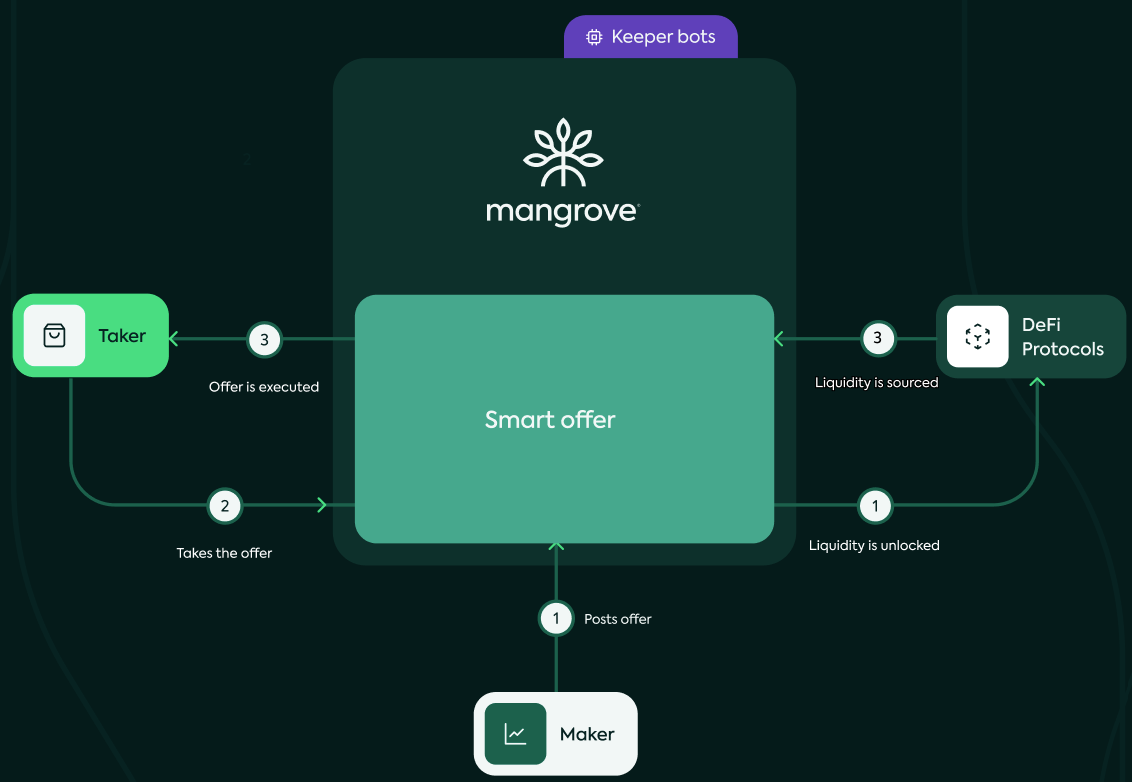
Makers, Takers, Keepers
In the Mangrove ecosystem, three key participants interact to facilitate a dynamic and decentralized trading environment: Makers, Takers, and Keepers. Together, they form the backbone of the Mangrove ecosystem, each playing a unique yet interconnected role in ensuring a seamless and effective trading experience.
Here is a simplified three-step diagram of Mangrove unlocked assets and offer-is-code approach. It also introduces the three main actors on Mangrove DEX.
Makers
Makers are participants or entities within the Mangrove ecosystem who are responsible for creating and listing offers on the platform. They can specify the conditions of their offers, such as the type and quantity of assets to be exchanged, the price, and any other relevant terms. For example, they promise to give a Taker some apples if he gives them oranges in return.
By initiating these offers, Makers enable transactions to occur within the Mangrove Protocol, contributing to a vibrant market.
Takers
Takers respond to the offers set up by Makers. They critically assess these offers, considering factors like asset types, quantities, and prices.
The role of Takers is crucial in completing transactions within the Mangrove marketplace. When a Taker agrees to the terms of an offer, they effectively seals the deal proposed by the Maker, leading to the execution of the trade.
Takers provide the necessary demand and liquidity in the marketplace, ensuring that the offers created by Makers are fulfilled. Their actions complete the cycle of trading activity within the Mangrove ecosystem, making it a dynamic and interactive platform for exchanges.
Takers have the ability to buy or sell assets on Mangrove, using either market or limit orders, akin to a traditional orderbook. They can execute these offers through general orders or choose to clean them individually.
This interaction between Takers and Makers completes the trading cycle in the Mangrove ecosystem, enhancing its interactivity and liquidity.
The workflow for Takers involves executing the logic of all relevant smart offers upon an order's placement. Successful orders are removed from the book, and the process continues until the Taker's order is completely filled. If a Maker withdraws their offer and fails to match the liquidity, the Taker is compensated with a penalty (bounty), and Mangrove proceeds to the next offer. This ensures that Takers are appropriately remunerated and that the order book remains efficient.
Keepers
Keepers functioning as automated bots that ensure the order book remains relevant and efficient. As market conditions evolve, the order book may become congested with outdated or irrelevant orders. Keepers play a pivotal role in addressing this by continuously monitoring the order book.
Their primary responsibility is to identify offers that are failing. Once a failing offer is detected, Keepers targets them to clean them off the book. This action involves setting a gas price in such a way that the offer’s bounty offsets the gas expenditure. Essentially, Keepers act as the custodians of the Mangrove ecosystem, maintaining its integrity and smooth operation.
In addition to managing failing offers, Keepers are tasked with keeping the gas price up to date. This is crucial for determining the compensation for Takers who remove a failing offer from the list. By doing so, Keepers ensure that Takers are appropriately remunerated for their role in sustaining the efficiency and cleanliness of the order book.
Through these functions, Keepers play an indispensable role in the maintenance and operational effectiveness of the Mangrove ecosystem, safeguarding its functionality and reliability.
Who is the Mangrove DEX for?
The Mangrove DEX offers a range of functionalities including market orders, limit orders, and the ability to deploy strategies, catering to different levels of DeFi users from beginners to experienced.
While market orders are accessible to all types of users, limit orders and amplified orders may be a bit more complex, and strategies are more suitable for experienced DeFi users.
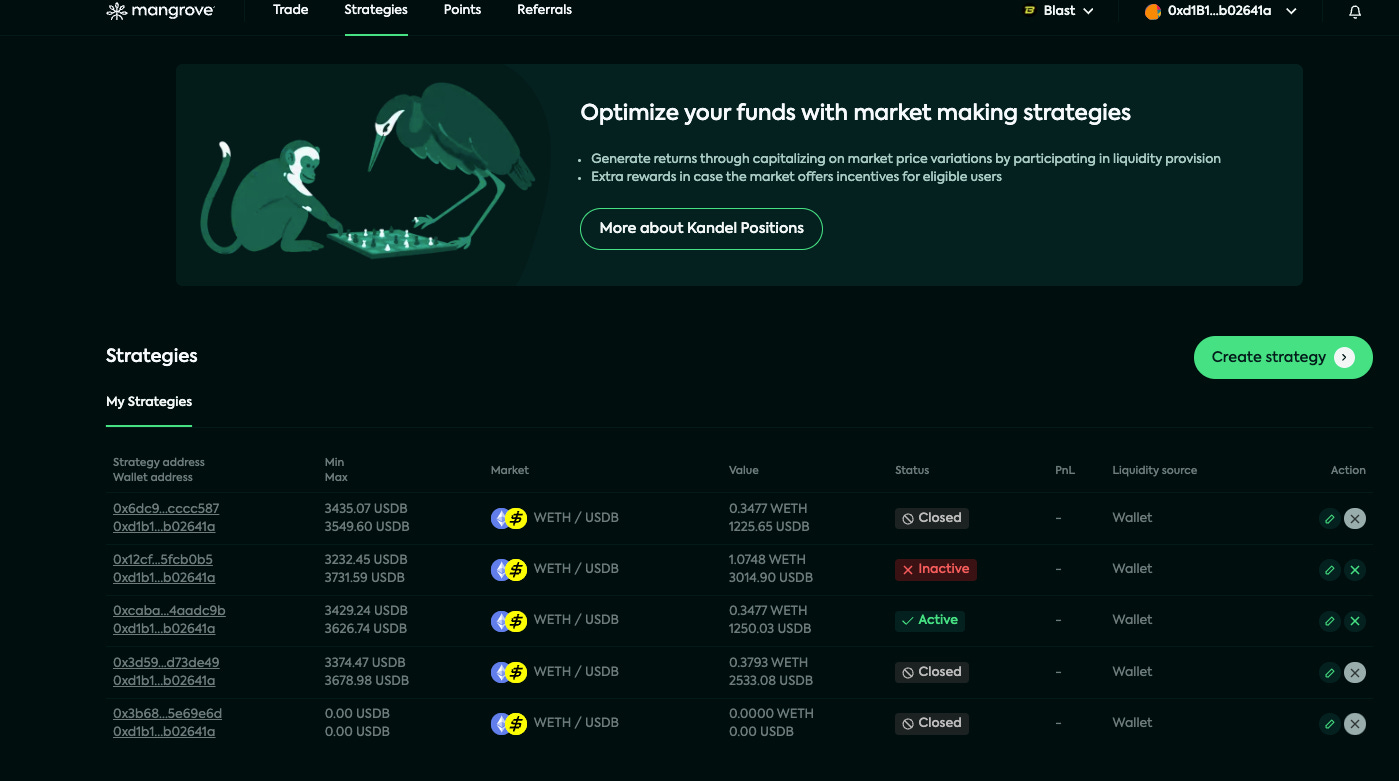
How to make a Kandel strategy on Mangrove
Mangrove allows liquidity providers, traders and strategists to deploy their own composable strategies. Strategies leverage Mangrove's core principles to incorporate defensive code, post unprovisioned offers, and redisplay liquidity after their offers are taken.
Currently, Mangrove has one available strategy for users: Kandel
Let’s go through it step by step.
Start by going to mangrove.exchange
Click on the "Create strategy" button on the "Strategies" tab and accept the Terms and Conditions after reading them.
Select a market and click on "Next."
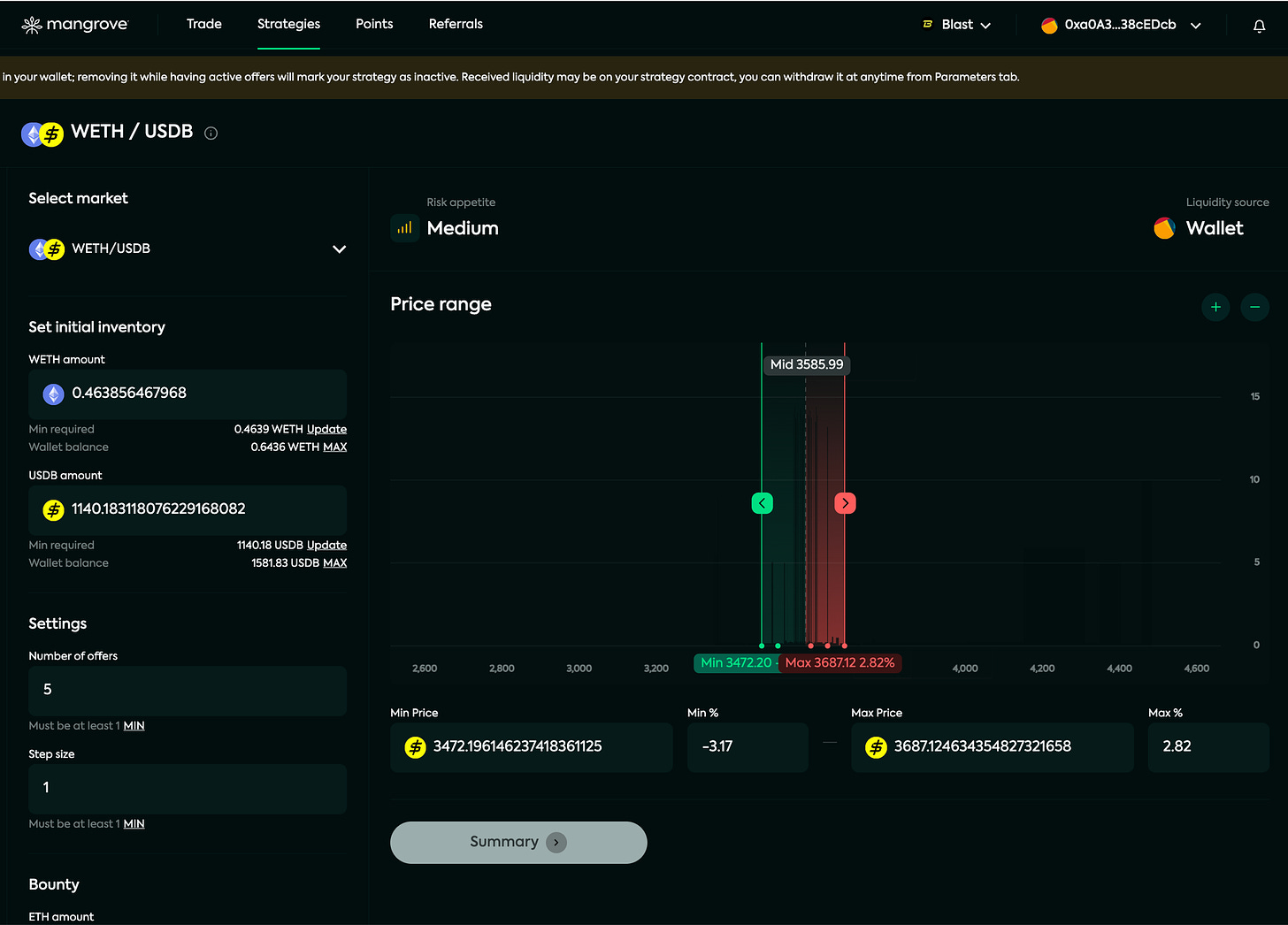
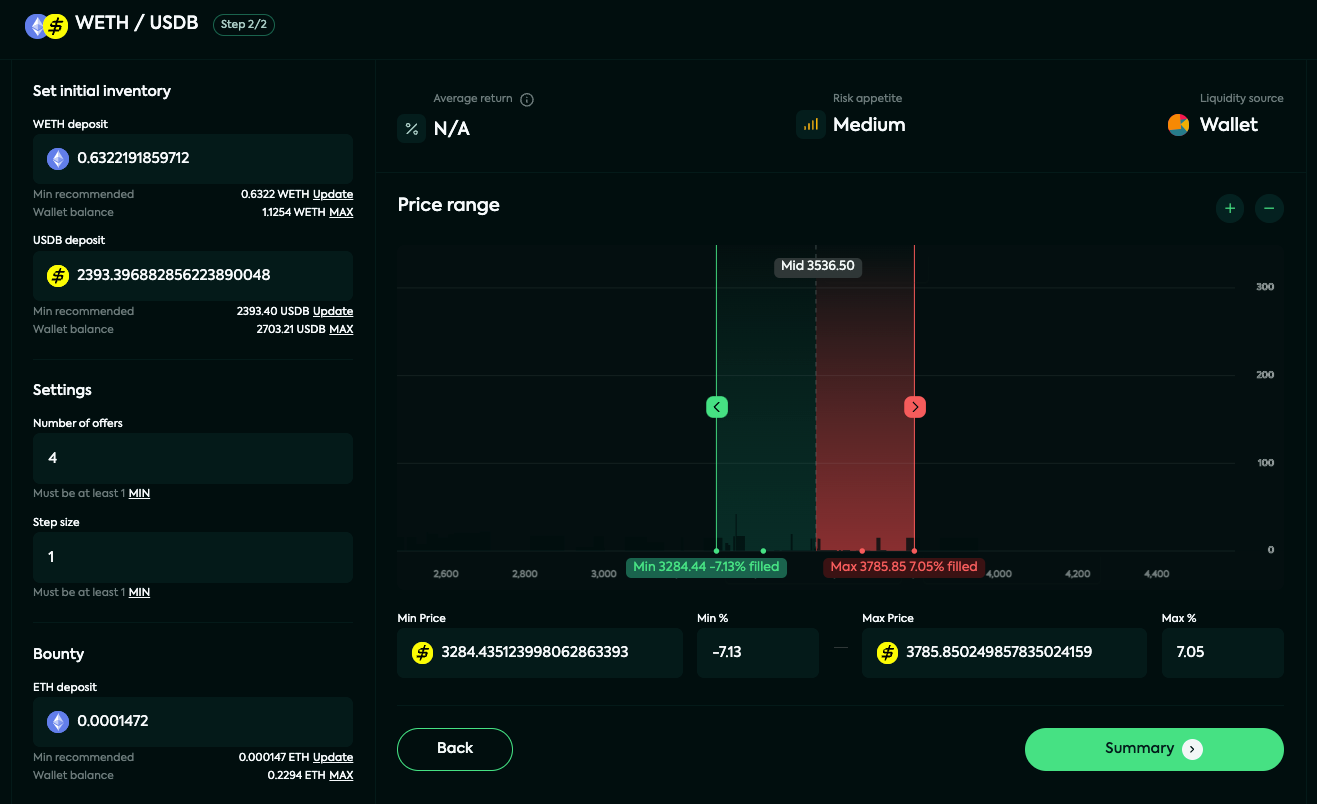
Determine your desired price range by dragging the limits on the market depth chart, setting the minimum and maximum price values, or using the percentage inputs. The market depth chart displayed on the strategy page allows you to see the real-time buy (Bids) and sell (Asks) offers on the Mangrove DEX for a given market.
Choose your initial inventory for both tokens.
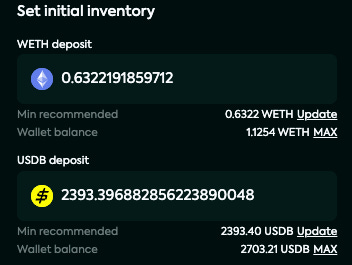
Choose the settings of your new Kandel strategy:
Number of price points
Step size
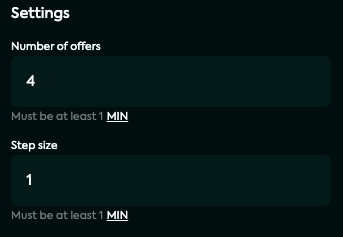
Choose a bounty amount.
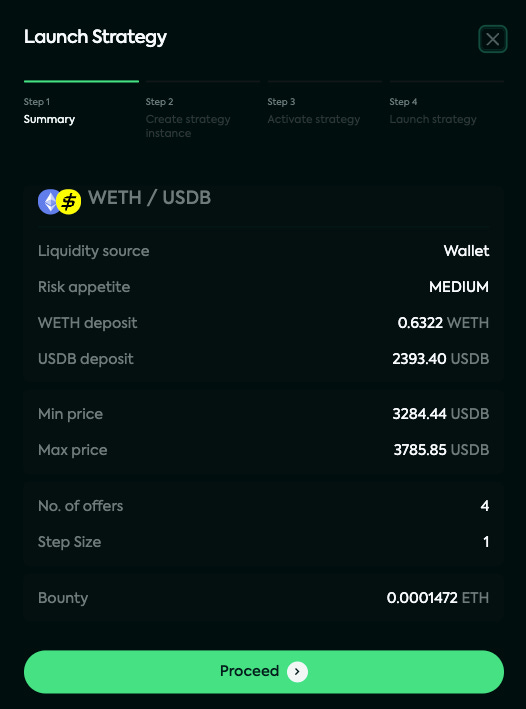
Click on "Summary".
Carefully review your strategy parameters:
If you want to edit them, close the pop-up or click away from it to go back to the strategy creation page
If you're ready to launch, click on "Proceed"
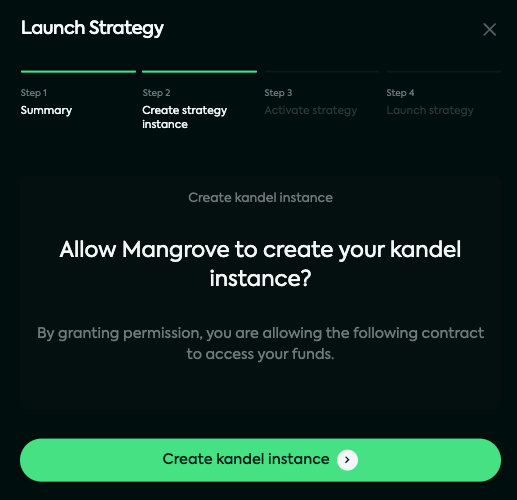
Each time you deploy a Kandel strategy, you are required to allow Mangrove to create a kandel instance on your behalf. Click on "Create kandel instance" to proceed.
What does this mean?
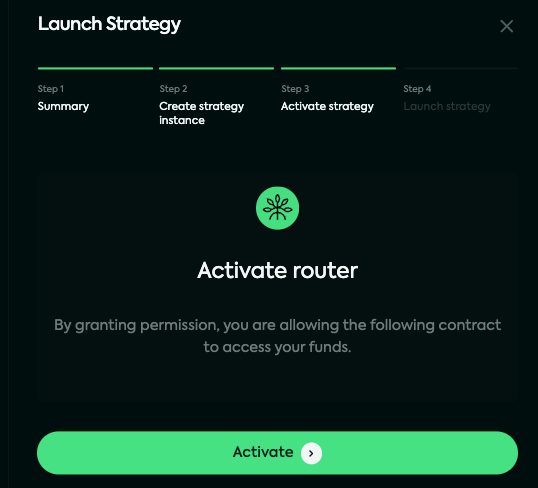
In order to leverage restaking of your liquidity, you first need to activate the liquidity sourcing router. Currently only sourcing from your wallet is available, but more liquidity sources will be added in the future.
If you have never used limit orders, amplified orders, or deployed a Kandel strategy on the selected market, you will be required to approve an allowance of the tokens involved in the strategy.
Click "Approve" to trigger the signing of 3 transactions in a row (including the deployment of your Kandel contract, the spending approvals of your pair's tokens).
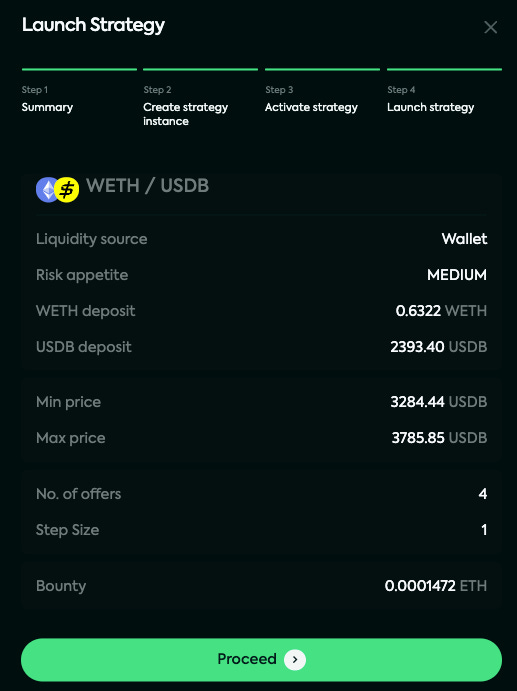
Click "Proceed" to launch your strategy.
Your Kandel strategy is now live and ready to start publishing buy and sell orders on the Mangrove order book.
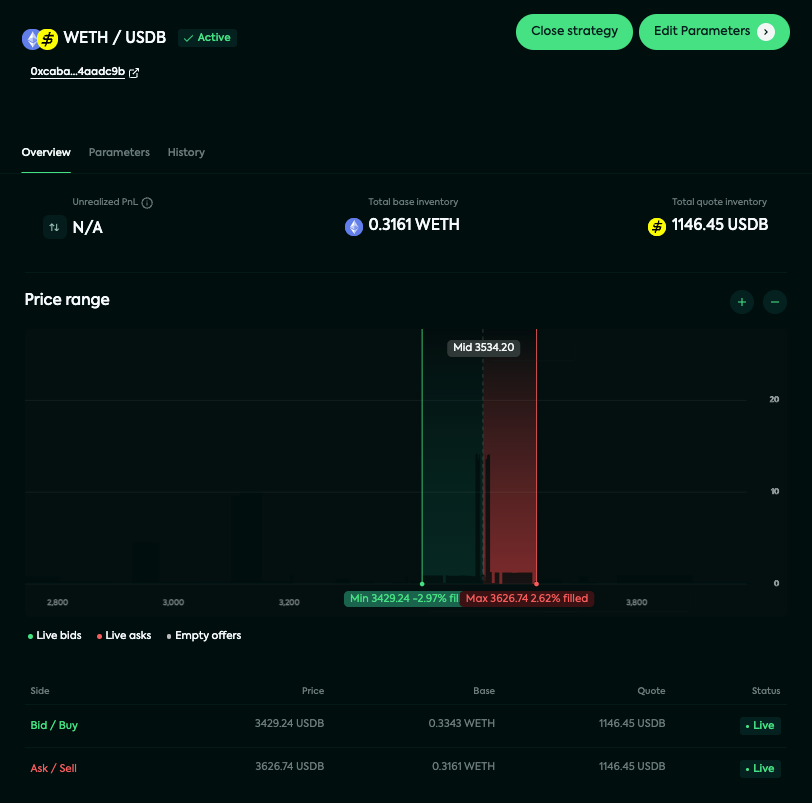
What do you do if you want to manage your Kandel strategy?
There are certain actions you can take by clicking the edit/manage button of your Kandel:
See your active offers and their statuses
Change your strategy parameters
Publish/unpublish the inventory of your strategy
See your parameter history
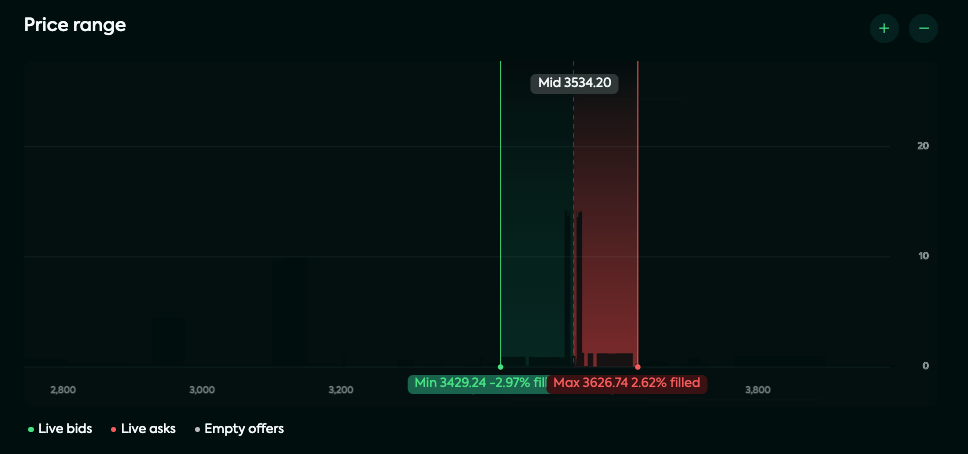
The overview page showcases a dynamic market depth chart for a specific market on the Mangrove DEX, presenting real-time buy (Bids) and sell (Asks) orders. This visual representation also highlights your strategy's price range and utilizes green, red, and gray dots to denote its offer price grid.
Green range: range for bids
Green dots: active bids
Red range: range for asks
Red dots: active asks
Grey dots: empty offers
Beneath the chart, you'll find your strategy's offer list, displaying:
the side (Bid/Ask)
the estimated price of base in quote
the quantities of base and quote
status of the offer
Now, let’s talk about risks-
Potential risks
Kandel strategy is subject to some risks that should be taken into consideration.
Economical risks
As a user of the Kandel strategy, you understand that using Kandel can be affected by economic risks, including but not limited to:
Partial or total loss of the tokens used;
Partial or total loss of the value of the tokens used;
Market extreme volatility;
Insolvency of a third-party platform or company;
Absence of liquidity and impossible resale on markets of the tokens.
Impermanent Loss
Kandel is a passive market-maker where profit is generated from the spread. An example of impermanent loss on an ETH/USDC pair would be as follows:
If the current price of ETH/USDC pair moves up, asks will be consumed.
If the price keeps going up and crosses the max price range value, Kandel strategy will be left only with active bid offers on the ETH/USDC market.
It is likely that no one would be interested in taking these bids since they would not match the current price (you would be offering too little USDC for ETH, considering the new current price). This is what we call impermanent loss - your strategy stops generating profit from the spread.
Smart contract and technological risks
Security error or failure allowing and/or resulting in hacking and stealing of user, third-party platform and/or website/app data;
Stealing or loss of the user external wallet private key or his access to the third-party platform;
Risks associated with blockchains used for the strategy, including but not limited to due to successful attacks from hackers or other criminal groups or organizations or countries, including but not limited to denial of service attacks, Sybil attacks, spoofing, smurfing malware attacks, consensus-based attacks, or phishing, or other new methods that may or may not be known;
Lack of transparency in crypto asset management and markets;
That being said, please note that the Kandel strategy has been thoroughly audited by ChainSecurity.
Conclusion
Mangrove is a DEX that is EVM-compatible and designed to improve the trading experience in DeFi. Its primary focus is addressing fragmented liquidity , high slippage, and under-utilized capital by providing responsive liquidity.
With their native strategy Kandel, anyone can become a market maker on the DEX. Over the coming weeks and months, Mangrove will expand the capabilities of the DEX by introducing additional trading pairs, improving the trading strategy functionalities as well as distribute Blast rewards to users.
…
All right, that’s it for today.
Let me know what you think about Mangrove and the rapid evolvement of DEXs in general.
Anyway, stay safe in the markets, anon!
Ciao.
Want To Sponsor This Newsletter? 🕴️
Send me a DM on Twitter: https://twitter.com/Route2FI or reply to this email. I have a sponsorship deck I can send you.
Join My Free Telegram Channel 🐸
I’ve launched a free Telegram channel where I share tweets, threads, articles, trades, blog posts, etc. that I find interesting within crypto.
Join it for free here: https://t.me/cryptogoodreads








Good write up. Thanks!